The Recoverer Process (RECO) is used to resolve failures of distributed transactions in a distributed database.
Consider a database that is distributed on two servers – one in India and one in Chicago.
Further, the database may be distributed on servers of two different operating systems, e.g. LINUX and Windows.
The RECO process of a node automatically connects to other databases involved in an in-doubt distributed transaction.
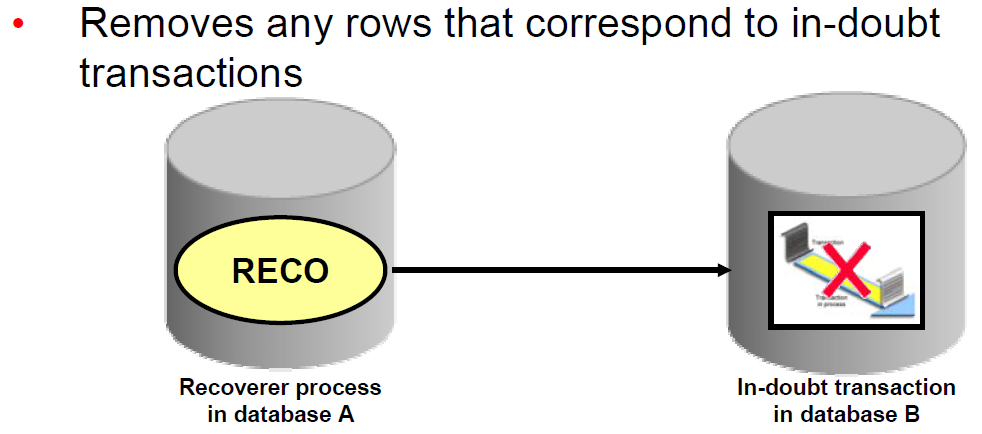
When RECO reestablishes a connection between the databases, it automatically resolves all in-doubt transactions, removing from each database's pending transaction table any rows that correspond to the resolved transactions.
Recoverer is responsible for recovering failed distributed transactions in a distributed database.
If the RECO process fails to connect with a remote server, RECO automatically tries to connect again after a timed interval. However, RECO waits an increasing amount of time (growing exponentially) before it attempts another connection. The RECO process is present only if the instance permits distributed transactions. The number of concurrent distributed transactions is not limited.
Consider a database that is distributed on two servers – one in India and one in Chicago.
Further, the database may be distributed on servers of two different operating systems, e.g. LINUX and Windows.
The RECO process of a node automatically connects to other databases involved in an in-doubt distributed transaction.
When RECO reestablishes a connection between the databases, it automatically resolves all in-doubt transactions, removing from each database's pending transaction table any rows that correspond to the resolved transactions.
Recoverer is responsible for recovering failed distributed transactions in a distributed database.
If the RECO process fails to connect with a remote server, RECO automatically tries to connect again after a timed interval. However, RECO waits an increasing amount of time (growing exponentially) before it attempts another connection. The RECO process is present only if the instance permits distributed transactions. The number of concurrent distributed transactions is not limited.

No comments:
Post a Comment