Connecting to an Oracle Instance (User Process & Server Process)
Before users can submit SQL statements to an Oracle database, they must connect to an instance.
User Process:
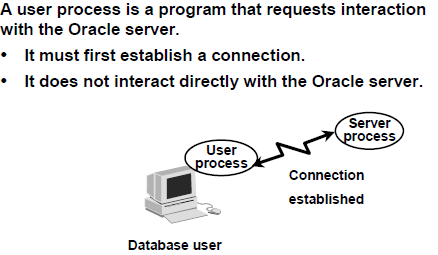
A database user who needs to request information from the database must first make a connection with the Oracle server. The connection is requested using a database interface tool, such as SQL*Plus, and beginning the user process. The user process does not interact directly with the Oracle server. Rather it generates calls through the user program interface (UPI), which creates a session and starts a server process.
Server Process:
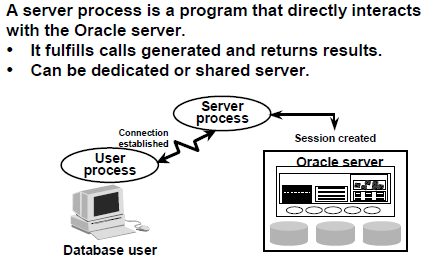
Connecting to an Oracle Instance:
The user starts a tool such as SQL*Plus,sql developer,toad or runs an application developed using a tool such as Oracle Forms. This application or tool is executed as a user process.
In the most basic configuration, when a user logs on to the Oracle server, a process is created on the computer running the Oracle server. This process is called a server process. The server process communicates with the Oracle instance on behalf of the user process that runs on the client. The server process executes SQL statements on behalf of the user.
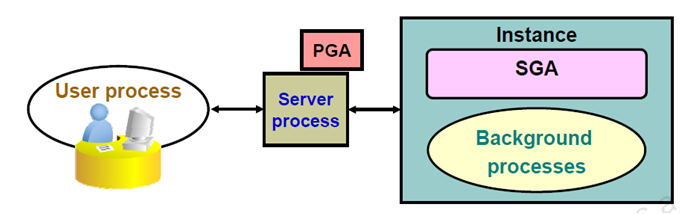
user process & server process are used to manage the execution of sql/plsql statements.
one-to-one correspondence between the User and Server Processes. This is called a Dedicated Server connection. An alternative configuration is to use a Shared Server where more than one User Process shares a Server Process.
Server Process is the go-between for a Client Process and the Oracle Instance.
Dedicated Server environment – there is a single Server Process to serve each Client Process.
Shared Server environment – a Server Process can serve several User Processes, although with some performance reduction
Connection
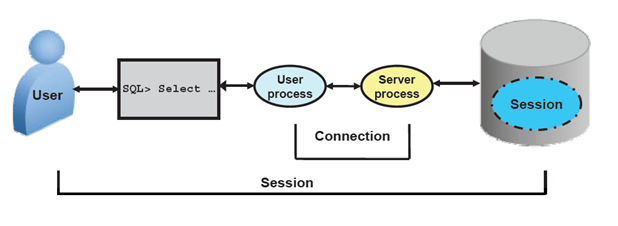
A connection is a communication pathway between a user process and an Oracle server. A database user can connect to an Oracle server using tool, sqlplus etc.
Sessions
A session is a specific connection of a user to an Oracle server. The session starts when the user is validated by the Oracle server, and it ends when the user logs out or when there is an abnormal termination. For a given database user, many concurrent sessions are possible if the user logs on from many tools, applications, or terminals at the same time.
No comments:
Post a Comment